The Blow-Fill-Seal Process
The Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) process is a widely used manufacturing technique in the pharmaceutical industry. It involves the simultaneous formation, filling, and sealing of containers, all within a single machine. This seamless and efficient process ensures the integrity and sterility of the final product, making it a preferred choice for aseptic packaging.
However, there is much more to this process than meets the eye. From the intricate machine components to the challenges posed by varying production volumes, the BFS process has its own set of complexities.
Key Takeaways
- Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) technology is a manufacturing process used in the pharmaceutical industry for aseptic packaging of injectable and sterile drug products.
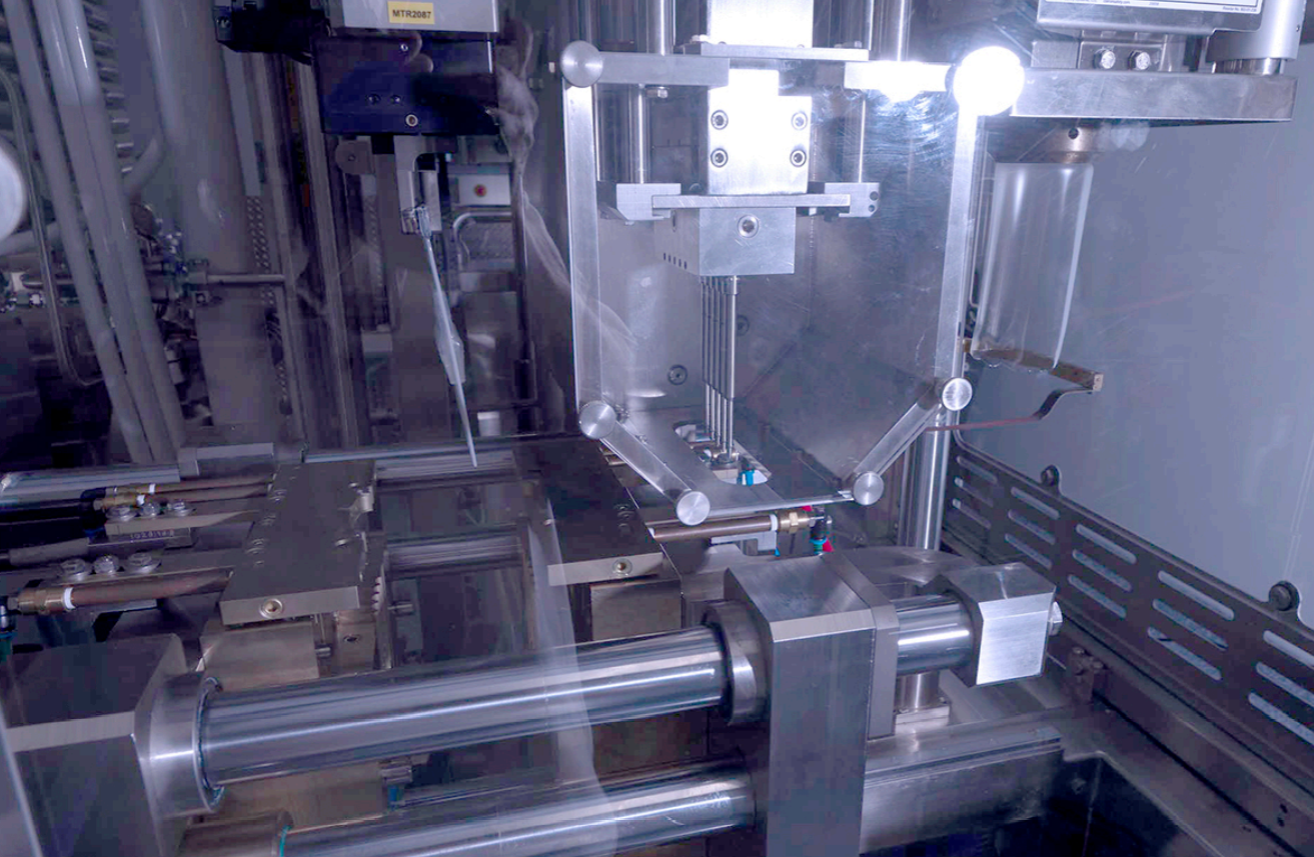
- The machine components of the BFS process, including mold cavity, blow molding machine, filling and sealing stations, and trimming station, ensure the production of high-quality containers.
- The actual manufacturing process of BFS containers involves extrusion, molding, filling, sealing, and demolding, all done under controlled temperature conditions.
- BFS technology offers flexibility to accommodate different production volumes and sizes of containers, optimizing efficiency and maintaining high-quality standards.
What is Blow-Fill-Seal?
Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) is a highly efficient and precise manufacturing process used in the pharmaceutical industry to produce sterile liquid-filled containers.
This Blow-Fill-Seal technology combines the three essential steps of container formation, filling, and sealing into one continuous operation. The BFS process involves a BFS machine that uses aseptic filling techniques to produce pharmaceutical liquids in a controlled and sterile environment.
This process is particularly suitable for the production of injectable products and sterile drug products, where the highest level of sterility and product quality is required.
The BFS technology eliminates the need for traditional container handling, reducing the risk of contamination and ensuring a consistent and reliable production process. By producing a completely sealed and sterile product, the BFS process helps to maintain the integrity and safety of pharmaceutical products, providing a reliable solution for the pharmaceutical industry.
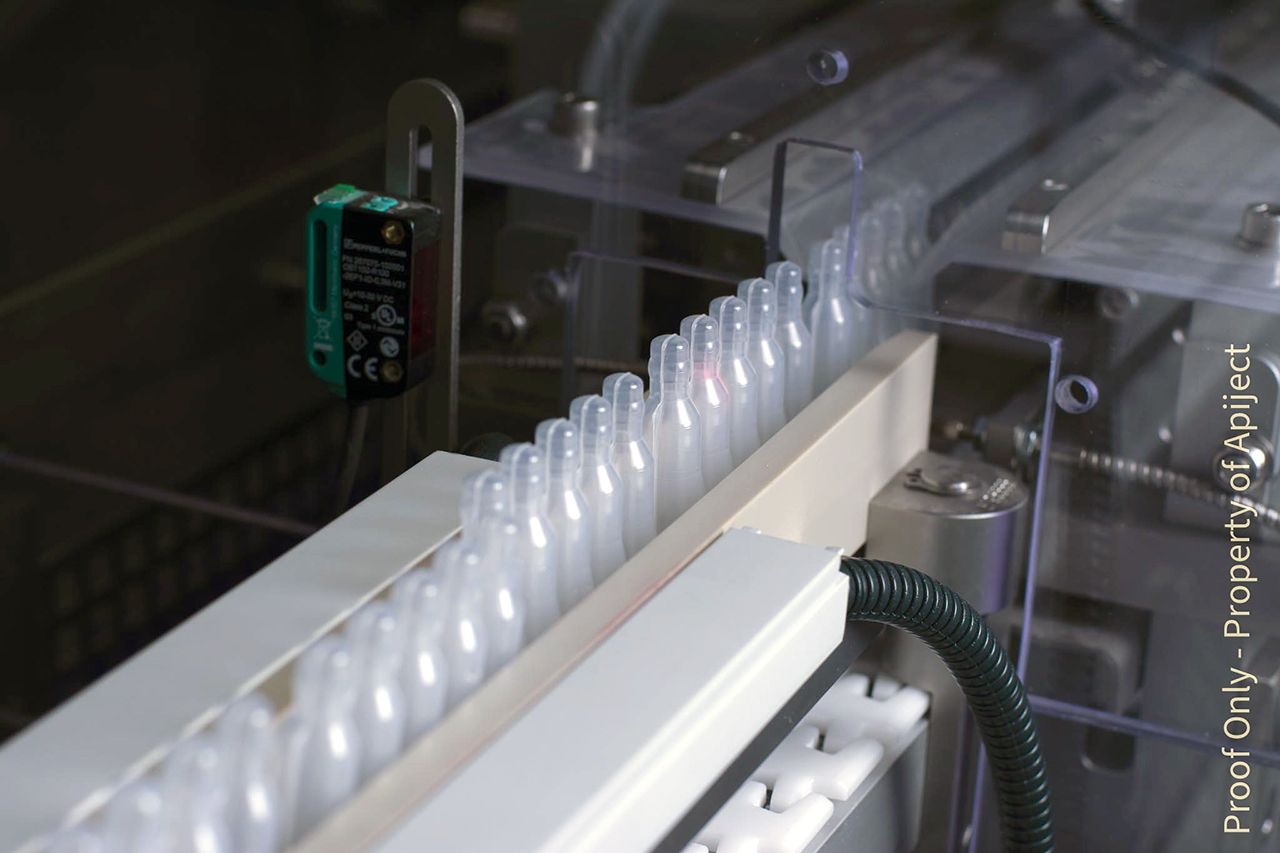
Overview of Machine Components
The machine components of the Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) process work in synchronization to ensure the efficient and precise production of sterile BFS containers in the pharmaceutical industry.
This aseptic filling process involves several key machine components.
First, the mold cavity is responsible for shaping the plastic containers.
The extrusion blow molding machine then shapes the container by blowing air into the mold.
The filling and sealing stations play a crucial role in filling the container with the desired pharmaceutical product and sealing it aseptically.
Finally, the trimming station removes any excess plastic from the container.
These machine components, when combined with BFS technology, are essential in the pharmaceutical manufacturing process, ensuring the production of high-quality primary containers for the pharmaceutical industry.
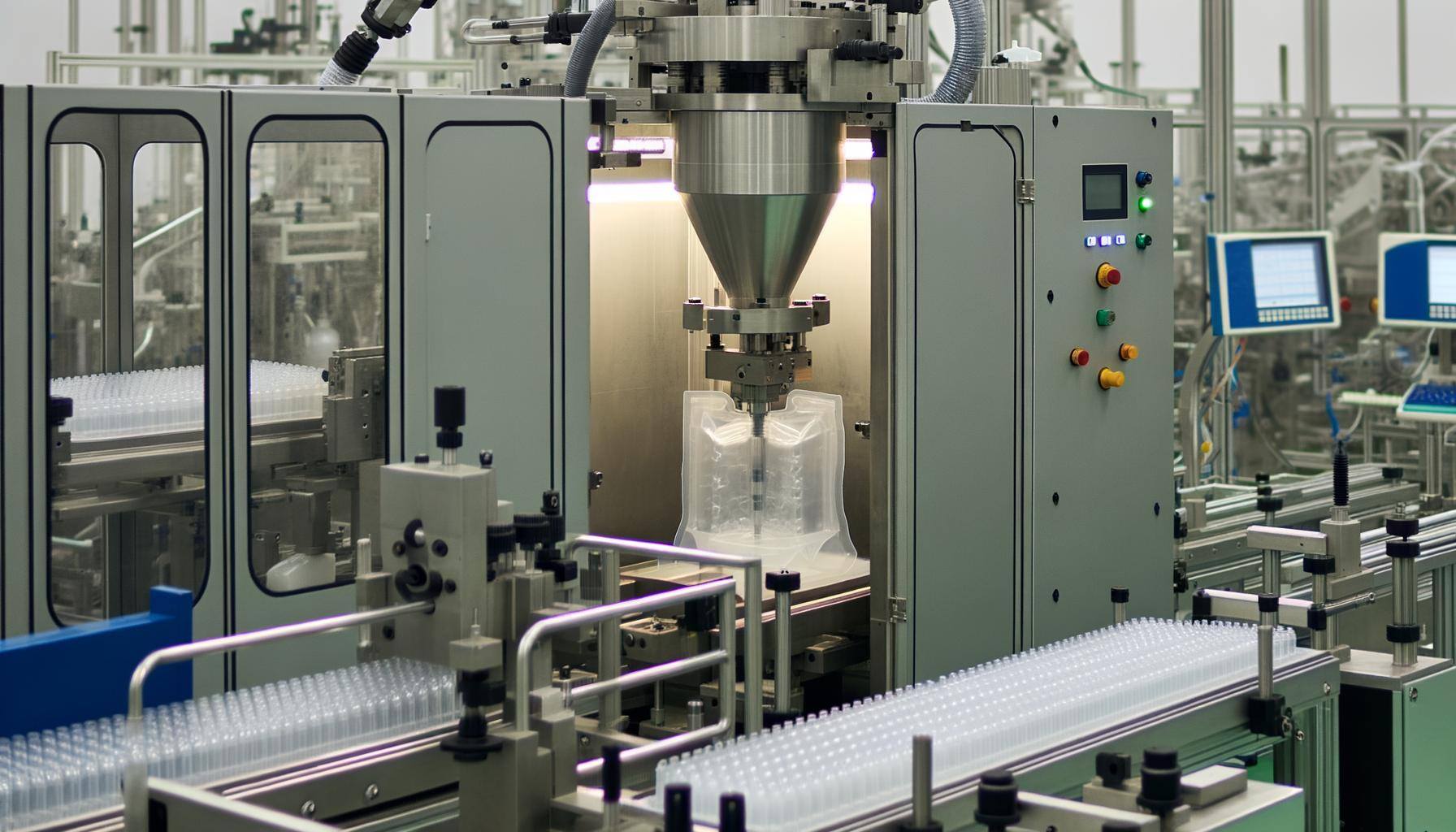
Actual Manufacturing Process
Having gained an understanding of the machine components involved in the Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) process, we can now delve into the actual manufacturing process of sterile BFS containers for the pharmaceutical industry. This aseptic process is a continuous and highly efficient technology used in the packaging process of pharmaceutical products.
The actual manufacturing process can be summarized as follows:
- Extrusion: A thermoplastic elastomer (TPE) is extruded into a tube, which serves as the starting material for the container.
- Molding: The tube is molded using a blow molding tool, where the bottom of the hose is welded, and the upper part is inflated to the shape of the mold.
- Filling: The aseptic filling process takes place as the product is introduced into the mold via a mandrel.
- Sealing: After filling, the mandrel is removed, and the container is sealed aseptically with the desired closure system.
- Demolding: The mold opens, and the finished product, a sterile BFS container, is removed.
- Release and inspection: The containers are released from the BFS machine and conveyed to the inspection area for quality control.
This continuous process allows for the production of a variety of container shapes while adhering to critical process parameters to ensure the sterility of the BFS containers.
Elevated Temperatures and Aseptic Filling
Elevated temperatures and the aseptic filling process are critical factors in ensuring the production of sterile BFS containers through the Blow-Fill-Seal technology. The Blow-Fill-Seal (BFS) process is widely used in pharmaceutical technology for packaging liquid products, such as ophthalmic and injectable products. To maintain sterility and integrity, the container design and aseptic processing technologies employed in BFS are carefully designed. One of the challenges in BFS is the need to heat the plastic pellets to high temperatures, around 180 degrees Celsius, to form the containers. However, the sterile liquid pharmaceuticals filled into these containers need to be maintained at much lower temperatures, typically 2-8 degrees Celsius. Therefore, the BFS machine and process must carefully control the temperature of both the container and the sterile liquid to prevent any adverse effects on the product's quality and efficacy.
Production Volume Variation
With regards to the Blow Fill Seal (BFS) process, another crucial aspect to consider is the impact of production volume variation. This factor has significant implications for the finished product and the overall efficiency of the Blow-Fill-Seal BFS technology.
Here are three key points to consider regarding production volume variation:
- BFS technology allows for the filling of a wide variety of single-dose containers, accommodating different production volumes efficiently and consistently.
- To ensure product quality, critical process parameters such as fill volume, temperature, and sealing pressure must be carefully controlled and adjusted based on the specific production volume.
- The flexibility of the BFS technology enables accurate and secure filling of different sizes of glass containers, ensuring high-quality results throughout the actual production process.
Understanding and managing production volume variation is essential for optimizing the efficiency and maintaining the desired quality standards in the aseptic filling operation of BFS technology.
Benefits of BFS Technology
BFS technology offers a range of benefits in aseptic pharmaceutical processing.
One of these benefits is the ability to have highly customizable container shapes and volumes for efficient and precise filling of liquid products. Unlike traditional glass vial manufacturing, which is limited in terms of shape and volume, BFS technology enables the production of plastic ampoules with various shapes and sizes.
This flexibility optimizes the use of space during manufacturing and storage, while also meeting the specific needs of different medications. Additionally, the use of BFS technology eliminates the risk of glass particulates or shards, making it a safer option for both healthcare professionals and patients.
This is particularly important for biological products and ophthalmic products, where the purity and safety of the liquid product are paramount. By reducing human intervention and ensuring efficient delivery, BFS technology improves the overall quality and reliability of aseptic pharmaceutical processing.
Top Questions Answered by Experts
What is the Form-Fill-Seal Process?
The form fill seal process is a type of packaging process used for various products, including food and non-food items. It involves the use of a flexible film or plastic to create a package that is then filled with the product and sealed. This process is efficient and cost-effective, as it reduces the need for additional packaging materials and labor.
What Are the Common Challenges Faced During the Blow-Fill-Seal Process?
During the blow-fill-seal process, common challenges include maintaining a sterile environment, ensuring accurate filling and sealing, preventing contamination, managing temperature and pressure, and optimizing production efficiency.
Are There Any Specific Quality Control Measures Implemented During the BFS Process?
Quality control measures are an integral part of any manufacturing process. In ensuring product safety and compliance, they play a crucial role. Implementing specific quality control measures during the BFS process helps maintain consistent product quality and minimize potential risks.
How Does the Blow Fill Seal Process Compare to Traditional Packaging Methods in Terms of Product Integrity?
When comparing the blow-fill-seal process to traditional packaging methods in terms of product integrity, it is important to consider the advantages and disadvantages of each approach.
Is the Blow-Fill-Seal Process Suitable for All Types of Pharmaceutical Products?
The suitability of the blow-fill-seal process for all types of pharmaceutical products is a matter of careful consideration. This involves assessing factors such as product characteristics, compatibility with the process, and regulatory requirements.


